Introduction
In the ever-evolving landscape of the food and beverage industry, technology has emerged as a powerful force driving innovation, efficiency, and customer engagement. Among the most transformative technologies are Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR), which are redefining how diners interact with food, restaurants, and culinary experiences. While traditional dining has focused primarily on taste, aroma, and presentation, AR and VR are adding immersive digital dimensions that enhance both the sensory and experiential aspects of eating.
AR and VR are no longer confined to gaming or entertainment; they are now revolutionizing multiple industries, including hospitality, retail, education, and tourism. Within the food sector, these technologies provide opportunities for interactive menus, virtual kitchens, enhanced food marketing, and even culinary training, creating experiences that are personalized, memorable, and technologically advanced.
This article explores the current applications, technological frameworks, and future potential of AR and VR in the dining industry. We will examine case studies of innovative restaurants, analyze consumer behavior, discuss the technological requirements, and forecast the long-term implications of immersive technologies on culinary business models.
1. Understanding AR and VR in the Food Industry
1.1 Definitions and Distinctions
Before delving into applications, it is crucial to differentiate between AR and VR:
- Augmented Reality (AR) overlays digital information onto the real world through devices like smartphones, tablets, or AR glasses. In dining, this could mean visualizing a dish in 3D on the table before ordering, seeing nutritional information, or exploring interactive recipes.
- Virtual Reality (VR) immerses the user in a fully digital environment, often through headsets such as Oculus Quest or HTC Vive. VR dining experiences may simulate virtual restaurants, culinary tours, or even interactive cooking lessons, transporting diners to environments they cannot physically access.
While AR enhances reality with digital elements, VR replaces reality with a simulated environment, and both technologies can be leveraged to provide unprecedented culinary experiences.
1.2 Consumer Trends Driving Adoption
Modern consumers, particularly millennials and Gen Z, seek unique and personalized experiences in dining, going beyond food quality alone. According to industry research:
- 70% of diners are interested in interactive or immersive dining experiences.
- Restaurants integrating AR or VR report higher customer engagement, increased social media shares, and brand loyalty.
- The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated digital adoption in restaurants, including virtual ordering, online food experiences, and contactless technologies, creating a fertile environment for AR and VR innovations.
The convergence of technology adoption and experience-driven dining makes AR and VR a strategic tool for restaurateurs aiming to differentiate themselves in a competitive market.
2. Applications of AR in Dining
2.1 Interactive Menus
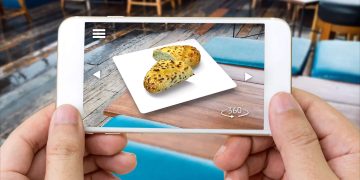
One of the most accessible and popular applications of AR in restaurants is interactive menu experiences. Traditional printed menus are static, but AR-enabled menus allow diners to:
- Visualize dishes in 3D before ordering. For instance, pointing a smartphone camera at a menu can display a life-sized rendering of the dish, showing ingredients, portion sizes, and presentation.
- Access nutritional information, allergy alerts, and sourcing details instantly.
- Explore customization options, such as swapping ingredients, adjusting portion sizes, or pairing wines with meals digitally.
AR menus not only enhance transparency but also reduce decision-making anxiety and increase customer satisfaction, especially in multicultural or high-end restaurants.
2.2 Interactive Table Experiences
Some restaurants are integrating AR into the dining table itself, creating immersive tabletop experiences. For example:
- AR tabletop projectors can display animated visuals of food origins, showing how ingredients are harvested or prepared.
- Interactive games, such as digital scavenger hunts or quizzes, can engage families and diners while they wait for their meals.
- AR surfaces can simulate environmental themes, turning a dining table into a virtual rainforest, underwater scene, or festive setting, enhancing the ambiance without expensive decor.
These innovations bridge the gap between dining and entertainment, encouraging diners to share experiences on social media, boosting marketing reach.
2.3 AR in Marketing and Storytelling
AR can also be leveraged outside the restaurant in marketing campaigns. Brands can:
- Use AR-enabled packaging that reveals cooking instructions, recipe suggestions, or interactive stories about the ingredients.
- Create immersive advertisements, allowing potential customers to explore dishes or restaurant interiors virtually before visiting.
- Offer loyalty programs or gamified experiences, where users can unlock digital rewards by scanning QR codes or engaging with AR content.
This type of experience-driven marketing strengthens brand engagement and encourages repeat visits.
3. Applications of VR in Dining
3.1 Virtual Restaurants and Immersive Dining
VR offers the possibility of creating entirely virtual restaurants that diners can explore from anywhere in the world. These experiences include:
- Simulated global dining: Diners can “visit” restaurants in Paris, Tokyo, or New York while seated in their living room, experiencing authentic ambiance and menu items virtually.
- Immersive themed experiences: Restaurants can offer VR dining events with fantasy, historical, or cultural themes, where diners interact with the environment while tasting real-world dishes prepared for delivery or in-house.
- Accessibility solutions: VR allows diners with mobility or geographic constraints to enjoy culinary experiences previously unavailable to them, expanding market reach.
3.2 Culinary Training and Staff Education
VR is transforming restaurant operations through training and education:
- VR simulations can train staff in table service, kitchen safety, or hygiene protocols without risk to real customers.
- Chefs can practice complex techniques or menu execution in a virtual environment, reducing training costs and errors.
- VR can simulate high-pressure service scenarios, preparing staff for peak hours or unexpected challenges.
The integration of VR in training ensures consistency, efficiency, and elevated service quality, indirectly enhancing customer satisfaction.
3.3 Virtual Food Festivals and Events
The VR space is being used to host virtual culinary festivals, connecting food enthusiasts, chefs, and brands globally:
- Attendees can explore virtual food stalls, watch cooking demonstrations, and interact with chefs in real time.
- VR allows for interactive tastings, where participants can see the preparation of a dish before ordering ingredients for home cooking.
- Virtual events reduce logistical costs, expand the audience, and provide data insights into consumer behavior.
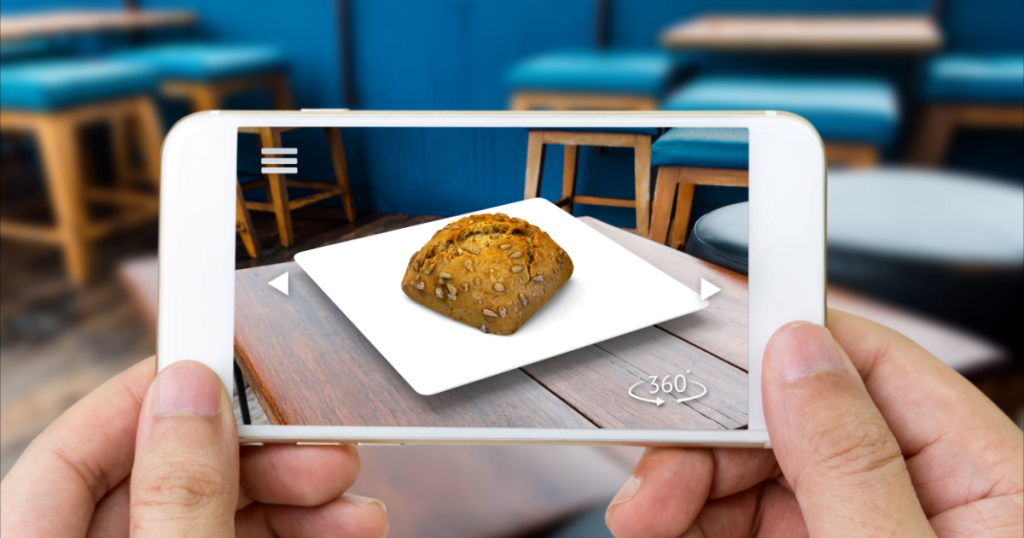

4. Technological Requirements and Integration
Implementing AR and VR in restaurants requires a combination of hardware, software, and creative design:
4.1 Hardware
- AR devices: Smartphones, tablets, AR glasses (e.g., Microsoft HoloLens, Magic Leap).
- VR devices: Headsets (Oculus Quest, HTC Vive, PlayStation VR), motion controllers, and haptic feedback systems for immersive interactions.
- Sensors and Projectors: For interactive tables or projection mapping experiences.
4.2 Software
- 3D modeling and animation: To create realistic food visuals and virtual environments.
- AR/VR platforms: Unity, Unreal Engine, Vuforia, ARKit, ARCore for application development.
- Integration with POS systems: Ensuring that interactive menus or VR ordering flows connect seamlessly with ordering and payment systems.
4.3 Design and User Experience
- Intuitive interfaces: Both AR and VR experiences must be easy to navigate for users of all ages.
- Responsive and low-latency interactions: Essential to prevent motion sickness in VR and maintain realism.
- Content localization: Menus, instructions, and experiences must be adapted to the language and cultural context of diners.
5. Case Studies of AR and VR in Restaurants
5.1 AR in Practice: Kabaq (Turkey)
Kabaq, a Turkish food-tech startup, developed AR menus allowing diners to visualize dishes in 3D before ordering. The platform reports higher customer satisfaction and order accuracy, especially for tourists unfamiliar with local cuisine.
5.2 VR in Practice: Ultraviolet by Paul Pairet (Shanghai)
Ultraviolet offers a multi-sensory VR-enhanced dining experience, combining immersive visuals, soundscapes, and synchronized scents to complement each dish. Guests report heightened flavor perception, demonstrating VR’s potential to influence taste experience.
5.3 AR for Marketing: McDonald’s AR Happy Meals
McDonald’s implemented AR features in its Happy Meal boxes, where children can interact with characters and games, increasing brand engagement and customer retention.
6. Benefits and Challenges
6.1 Benefits
- Enhanced customer engagement: Immersive experiences increase brand recall and satisfaction.
- Educational value: Diners learn about ingredients, preparation, and cultural context.
- Marketing leverage: AR/VR experiences are highly shareable on social media, boosting reach.
- Operational efficiency: VR training reduces errors, speeds up onboarding, and improves service quality.
6.2 Challenges
- High initial investment: AR/VR equipment and content development can be costly.
- Technical literacy: Staff and customers must be comfortable with digital interfaces.
- Integration complexity: Seamless connection with POS and delivery systems is required.
- Overstimulation risk: Poorly designed experiences can distract from the food itself.
7. The Future of AR and VR in Dining
The convergence of AR, VR, and AI promises a future of hyper-personalized dining experiences:
- AI-powered AR menus could recommend dishes based on dietary preferences and health data.
- VR global gastronomy tours may allow diners to virtually “travel” to culinary destinations.
- Mixed Reality (MR) experiences will combine real and virtual food interactions for immersive storytelling.
- Sustainability education: AR and VR can teach diners about sustainable sourcing, waste reduction, and responsible consumption while dining.
As technology evolves, digital gastronomy may become as important as taste, presentation, and service in shaping the modern dining experience.
Conclusion
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) are redefining the restaurant industry by creating immersive, personalized, and interactive dining experiences. From AR menus and tabletop interactions to VR culinary tours and staff training, these technologies enhance engagement, education, and operational efficiency.
While challenges like cost, integration, and user adoption exist, the potential benefits in customer experience, brand loyalty, and marketing innovation are undeniable. As restaurants continue to embrace digital transformation, AR and VR will play an increasingly central role in shaping the future of dining, turning meals into multi-sensory experiences that delight the palate and stimulate the imagination.
By adopting AR and VR, the food industry is not only transforming how we eat, but also how we experience, learn about, and connect with food—ushering in a new era of digital gastronomy.